Symmetrical Balance: a type of balance in which both sides of an artwork look the same or almost the same.
·
Salvador Dali, Restrospective Bust of a Woman
Asymmetrical Balance: a type of balance in which the two sides of an artwork are not exactly alike, but are still visually balanced.
David Smith, Cubi X
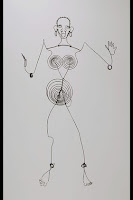
Radial Balance: occurs when objects are positioned around a central point.
·
·
Scale & Proportion: defines size relationships, or the illusion of correct size relationships between objects and figures.
Claes Oldenburg, Big Sweep
Emphasis: refers to a visual composition with an accent and direct attention or focal point.
Alexander Calder, A Universe
Alexander Calder, Lobster Trap and Fish Tail
Alexander Calder, Josephine Baker (III)
Jean (Hans) Arp, Birds in an Aquarium
Constantin Brancusi, Beginning of the World
Contrast: refers to the difference in visual properties that makes an object (or its representation in an image) distinguishable from other objects and the background.
Robert Rauschenberg, Untitled
Claes Oldenburg, Geometric Mouse, Scale A
Ellsworth Kelly, Green Blue
Anne Truitt, Twining Court I
Sol LeWitt, Floor Sculpture
Variety: refers to a way of combining elements of art in involved ways to achieve intricate and complex relationships.
Bruce Nauman, Human/Need/Desire
Constantin Brancusi, Maiastra
Sophie Taeuber-Arp, Dada Head
Vladimir Baranoff-Rossine, Symphony Number 1
John Chamberlain, Essex
Repetition: refers to a way of combining elements of art so that the same elements are used over and over again.
Louise Nevelson, Sky Cathedral
Ellsworth Kelly, Sculpture for a Large Wall
Alberto Giancometti, The Palace at 4 a.m.
Marcel Duchamp, Rotary Demisphere
Marcel Duchamp, Bicycle Wheel










































No comments:
Post a Comment